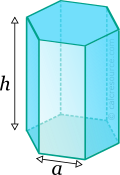
Properties of Hexagonal Prism
This tool calculates the basic geometric properties of a right prism, with a regular hexagonal base. Enter the shape dimensions 'a' and 'h' below. The calculated results will have the same units as your input. Please use consistent units for any input.
a = | |||
h = | |||
Geometric properties: | |||
Volume = | |||
Surface area = | |||
Base area = | |||
Lateral surface area = | |||
 |
ADVERTISEMENT
Definitions
Geometry
The prism is a solid object enclosed by two parallel planar polygonal bases and a lateral prismatic surface. Hexagonal prism is a special case of the general prism, which may have any arbitrary polygonal base. With a hexagon base, the number of faces, edges and vertices (NF, NE, NV respectively) is given by the formulas:
The volume of a prism is given by the formula:
where the surface area of the base and h the height of the prism. For regular hexagon, the base area is given by:
where the length of an edge of the base hexagon.
The surface area of one lateral face of the prism, is equal to:
Since there are 6 lateral faces and two bases, the total surface area of the hexagonal prism is: